Fact sheet
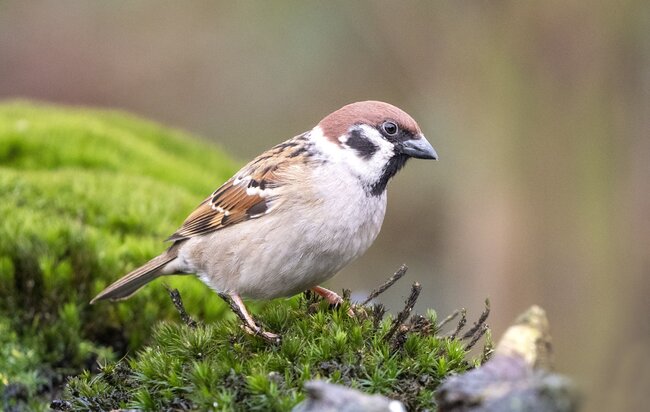
- Passer montanus
- Color: brown, black, white cheek with dark spot
- Size: 14 cm
- Age: up to 12 years
- Food: seeds
- scattered
- like to use birdhouses in winter

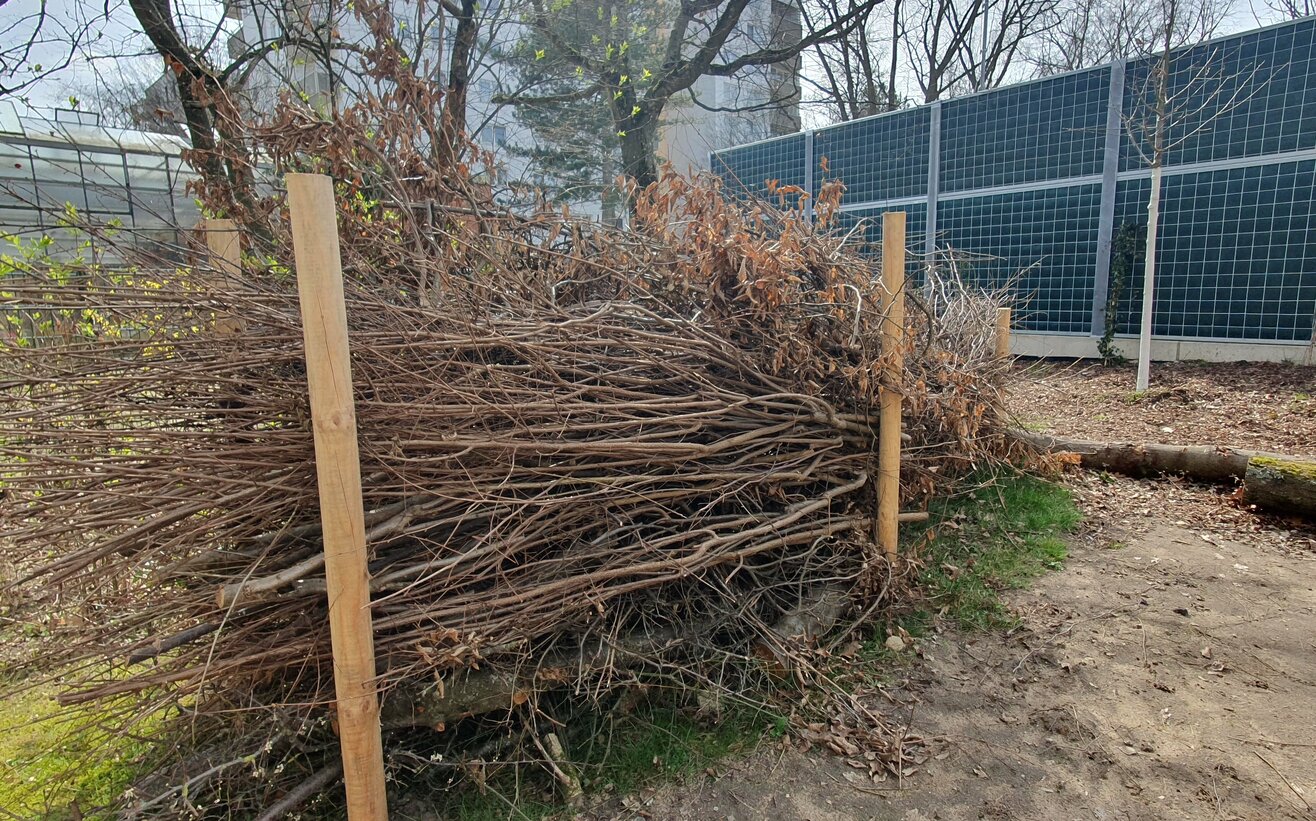
Deadwood hedge
Here live Eurasian tree sparrows
The tree sparrow, also known as the sparrow, is a typical example of an animal species that has adapted to human habitats. The sparrow is easily recognized by its loud call. As it is not shy, it can often be seen dust-bathing or foraging on the ground. The tree sparrow feeds mainly on grass seeds, herbs and cereals as well as buds and berries. During the breeding season, it prefers insects as food, which it finds on perennials or in meadows, shrubs and trees.
A deadwood hedge offers numerous advantages for animals such as the tree sparrow. The hedge serves as a valuable habitat as it provides protection from predators and extreme weather. The dense structure of branches and twigs provides excellent protection for the bird. Hedges, conifers and shrubs provide communal roosts, which are used particularly in the fall and winter. The tree sparrow finds plenty of food, such as insects and seeds, in and around the deadwood hedge. Other animals such as hedgehogs, lizards and numerous insects are also at home here.
As the deadwood is slowly decomposed by fungi and bacteria, humus is created, which has a positive effect on soil fertility as a fertilizer. Deadwood hedges also serve as natural wind and erosion protection and promote structural diversity in gardens or landscapes.
Deadwood hedges can also serve as a climbing aid for climbing plants such as blackberries and thus quickly form dense hedges.
Such hedges promote biodiversity and are a sustainable and near-natural solution in horticulture.